Introduction
Hello, I’m looking for a way to create a beam property for C-type channel material in Femap using Excel VBA! In this article, we will discuss how to use Excel VBA to automatically create beam properties for C-type channel material in Femap.Femap is a powerful tool for utilizing the Finite Element Analysis (FEA), but manually entering beam properties can be time consuming. So, use Excel VBA to improve efficiency.
Code for creating beam properties of C-type channel material
FEMAP also provides an API for creating properties. This can be used to create a variety of properties.
By the way, before creating a beam, you need to create a material. Please refer to the following related article on how to create materials from Excel.
Now, here is an example of VBA code that creates a new C-type beam in FEMAP.
The code must be run after FEMAP has been started.
Sub CreatCBeam
'Create Femap model object
Dim f As Object
Set f = GetObject(,"femap.model")
'Create property object
Dim pr As Object
Set pr = f.feProp
'Variable for return code
Dim rc As Long
'Input for shape (for C-type section)
Dim shape(5) As Double
shape(0) = 150 'Height input. In this case, the height is 150.
shape(1) = 75 'Top width input. In this case, the width is 75.
shape(2) = 75 'Bottom width input. In this case, the width is 75.
shape(3) = 12.5 'Top thickness input. In this case, the thickness is 12.5.
shape(4) = 12.5 'Bottom thickness input. In this case, the thickness is 12.5.
shape(5) = 9 'Thickness of the central vertical web. In this case, the thickness is 9.
'Set orientation direction. 0: Right, 1: Up, 2: Left, 3: Down
Dim orient As Long
orient = 0
pr.title = "150X75X9X12.5 C" 'Set the title. In this case, it is "150X75X9X12.5 C".
pr.matlID = 1 'Set the material ID. In this case, it is 1.
pr.Type = 5 'Set the type. For beams, set to 5.
'Create property
rc = pr.ComputeStdShape(10, shape, orient, 0, True, True, False) 'Arguments are: shape ID, section definition parameters, orientation, section evaluation method, shear center offset calculation, twist constant calculation, stress extraction position
pr.Put(1) 'Register the created property under property ID 1.
'Release objects
Set pr = Nothing
Set f = Nothing
if rc = 0 then
MsgBox "Property creation failed"
else
MsgBox "Property created successfully"
End If
End Sub- Lines 4-5 create the Femap object; note that executing this code when FEMAP is not running will result in an error.
- Lines 8-9 create the property object of the Entity object.
- Line 12 is the creation of the variable used to receive the return code, which should be of type Long.
- Lines 15-21 are the input of the shape, which should be of type Double.
- Lines 24-25 are the orientation direction inputs, of type Long, and should be integers from 0 to 3.
- The orientation direction is 0: right, 1: up, 2: left, 3: down, and so on.
- Line 27 assigns the title, using the String type.
- Line 28 assigns the material ID, which is of type Long.
- Line 29, “.Type” is used to input the type. In this case, we are creating a beam, so we specify “5”.
- ComputeStdShape()” on line 32 creates the property.
The seven arguments are, from left to right: shape ID (set to 10 since this is a C-shaped cross-section), cross-section definition parameter array, orientation direction, cross-section evaluation method, shear center offset variable, torsion constant calculation, and stress extraction position.
The cross-section evaluation method is specified by a Long type: 0: Automatic, 1: Original, 2: Alternative cross-section performance, and 3: Nastran PBEAML.
Shear center offset is specified by Boolean; if True, shear center offset is calculated.
Torsion constant calculation is a Boolean; if True, torsion constants are calculated.
The stress takeoff location is also specified as a Boolean; if True, the calculation will use the stress takeoff location and orientation currently defined for the object; if False, the stress takeoff location and orientation will be the default. - Line 33, “.Put()” registers the generated property with the specified property ID.
- Lines 36-37 are object release. There is no problem without it. When creating a large program, it is better to release unneeded objects in this way to make the program lighter.
- Lines 39-43 return 0 if the property is not created.
Example of linking with Excel sheet
To create a property for a C-type channel material beam with the values entered in an Excel sheet
Prepare the following sheet in Excel.
The input columns are A2 to J2.
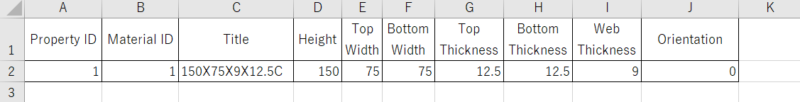
The code to create a property with each value entered on the above sheet is as follows
Sub CreatIBeam
'Create Femap model object
Dim f As Object
Set f = GetObject(,"femap.model")
'Create property object
Dim pr As Object
Set pr = f.feProp
'Variable to store return code
Dim rc As Long
'Input for shape dimensions (for -type section)
Dim shape(5) As Double
shape(0) = Cells(2,4) 'Input for height
shape(1) = Cells(2,5) 'Input for top width
shape(2) = Cells(2,6) 'Input for bottom width
shape(3) = Cells(2,7) 'Input for top thickness
shape(4) = Cells(2,8) 'Input for bottom thickness
shape(5) = Cells(2,9) 'Input for thickness of central vertical web
'Set orientation direction. 0: Right, 1: Up, 2: Left, 3: Down
Dim orient As Long
orient = Cells(2,10)
pr.title = Cells(2,3) 'Input for title
pr.matlID = Cells(2,2) 'Input for material ID
pr.Type = 5 'Set type. For beams, use type 5.
'Create property
rc = pr.ComputeStdShape(10, shape, orient, 0, True, True, False) 'Arguments: shape ID, section definition parameters, orientation, section evaluation method, shear center offset calculation, twist constant calculation, stress extraction position
pr.Put(Cells(2,1)) 'Property ID. Register the created property under the specified ID.
'Release objects
Set pr = Nothing
Set f = Nothing
if rc = 0 then
MsgBox "Property creation failed"
else
MsgBox "Property created successfully"
End If
End SubExample of exporting property information to Excel
You can also export the property information of Femap to Excel. for C-type beam, you can get the following values.
First, prepare an Excel sheet as shown below.
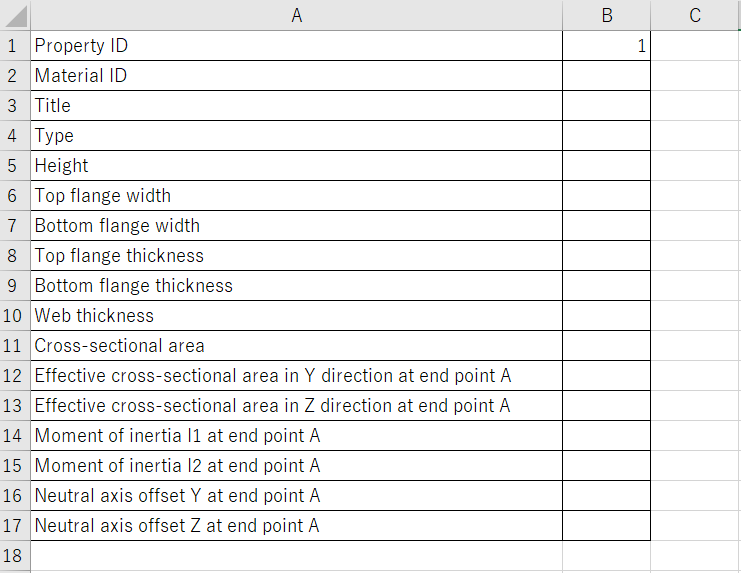
Enter only the number of the property ID you want to retrieve in the sheet above.
The VBA code will look like this
By executing this code, you can retrieve the property information in each blank field.
Sub GetBeamProperty()
On Error GoTo OUT1
'Create FEMAP model object
Dim f As Object
Set f = GetObject(,"femap.model")
On Error GoTo OUT2
'Create property object
Dim pr As Object
Set pr = f.feProp
Dim rc As Long 'Return code
pr.Get(Int(Cells(1,2))) 'Retrieve property ID entered in cell B1
Cells(2,2) = pr.matlID 'Retrieve material ID
Cells(3,2) = pr.title 'Retrieve title
Cells(4,2) = pr.Type 'Retrieve type. If it's a beam element, the value will be 5.
'If the retrieved property is a beam, retrieve the following values as well
If pr.Type = 5 Then
Cells(5,2) = pr.pval(40) 'General section height
Cells(6,2) = pr.pval(41) 'General section top width
Cells(7,2) = pr.pval(42) 'General section bottom width
Cells(8,2) = pr.pval(43) 'General section top thickness
Cells(9,2) = pr.pval(44) 'General section bottom thickness
Cells(10,2) = pr.pval(45) 'General section central web thickness
Cells(11,2) = pr.pval(0) 'Endpoint A section area
Cells(12,2) = pr.pval(5) 'Endpoint A Y effective section area
Cells(13,2) = pr.pval(6) 'Endpoint A Z effective section area
Cells(14,2) = pr.pval(1) 'Endpoint A I1
Cells(15,2) = pr.pval(2) 'Endpoint A I2
Cells(16,2) = pr.pval(16) 'Endpoint A neutral axis offset Y
Cells(17,2) = pr.pval(17) 'Endpoint A neutral axis offset Z
Else
MsgBox "This property " & Cells(1,2) & " is not a beam."
End If
'Release objects
Set pr = Nothing
Set f = Nothing
Exit Sub
OUT1:
MsgBox "Please launch FEMAP"
Exit Sub
OUT2:
MsgBox "Unknown error"
End Sub
- The property is obtained by “.get(property ID)” on line 15. It is better to specify the type with Int() to prevent errors. (The same is true for other cases of taking values from cells.)
- Various information is obtained by “.pval(number)” in lines 23-35. The number is determined by the information to be obtained, and in the case of a beam, it is as shown in the above comment.
Conclusion
With the method presented here, you can use Excel VBA to automatically create channel material for beams in Femap, and by utilizing VBA, you can create multiple beams at once and quickly change settings. If you are interested, please give it a try.

Having trouble creating channel sections? First, align your channels in Excel!




コメント